Introducing pydaasiot: Python bindings for DaaS-IoT
Introduction
We’re excited to announce the release of pydaasiot — the official Python bindings for the DaaS-IoT SDK. With pydaasiot, the core capabilities of DaaS-IoT are now accessible from Python, enabling seamless integration of distributed communication, time synchronization, and overlay networking into Python-based systems.
Built for Developers, Ready for Production
The DaaS-IoT SDK is engineered for high-performance IoT deployments. It provides a robust abstraction for overlay communication between devices, with support for multiple link types, time synchronization, and data delivery mechanisms. Until now, these capabilities were only available through C++.
With pydaasiot, you get the same low-latency, event-driven architecture in Python — without the overhead of dealing with native code or cross-language wrappers. This is ideal for rapid prototyping, algorithm testing, or embedding reliable device communication inside Python-powered pipelines.
Key Features
Full Python Access
Complete access to DaaS-IoT primitives directly in Python with native Python interfaces.
Event-Driven Architecture
Utilize Python callbacks for handling events, incoming data, and synchronization events.
Cross-Platform Support
Prebuilt wheels available for Windows and Linux with consistent API across platforms.
Network Abstraction
Support for various drivers including INET4, Bluetooth, and other communication links.
Practical Integration: Sender/Receiver Setup in Python
Here’s what real-world usage looks like using pydaasiot.
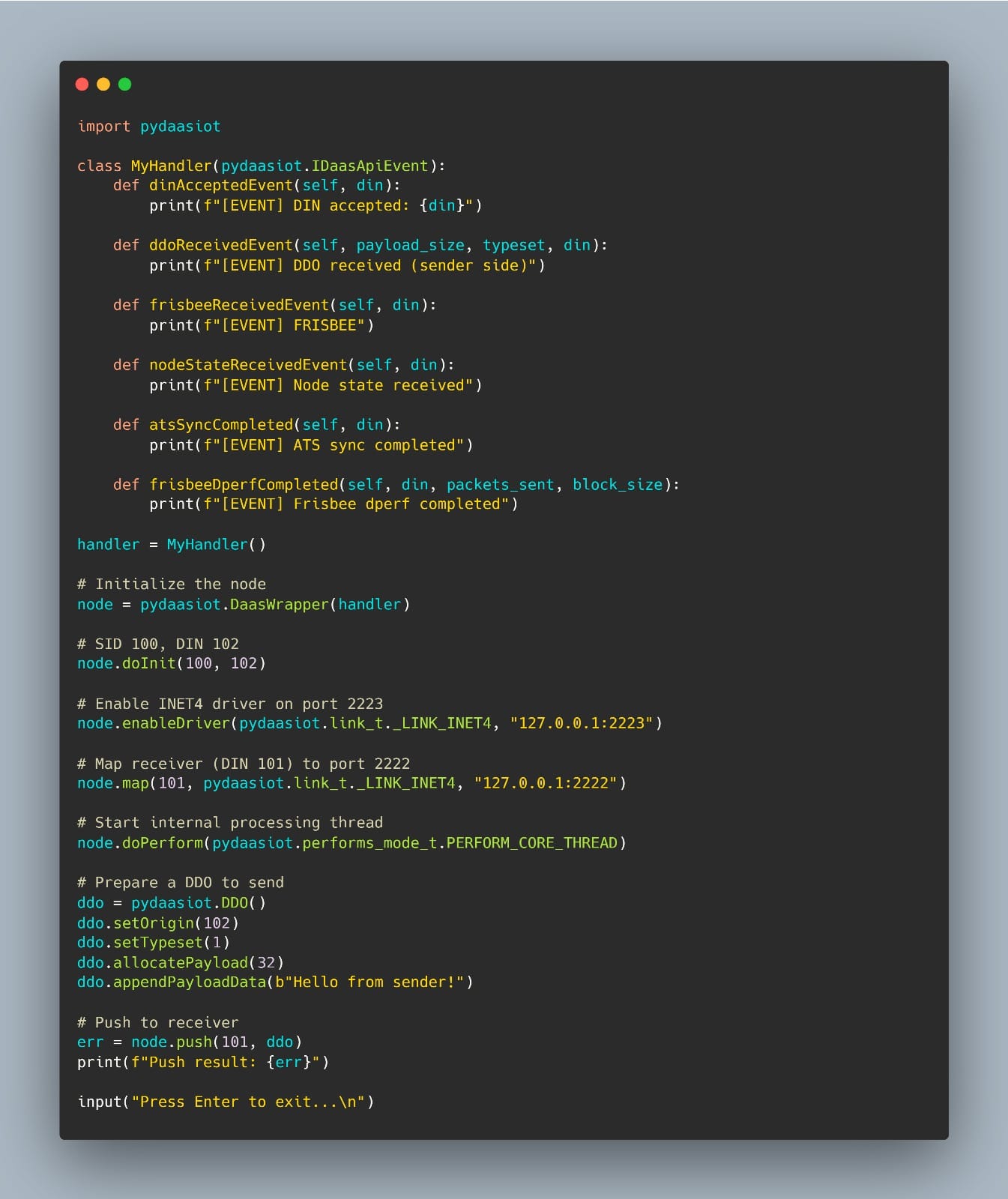
1. A sender node initialized, sets up a network driver, and pushes a DDO to a mapped destination.
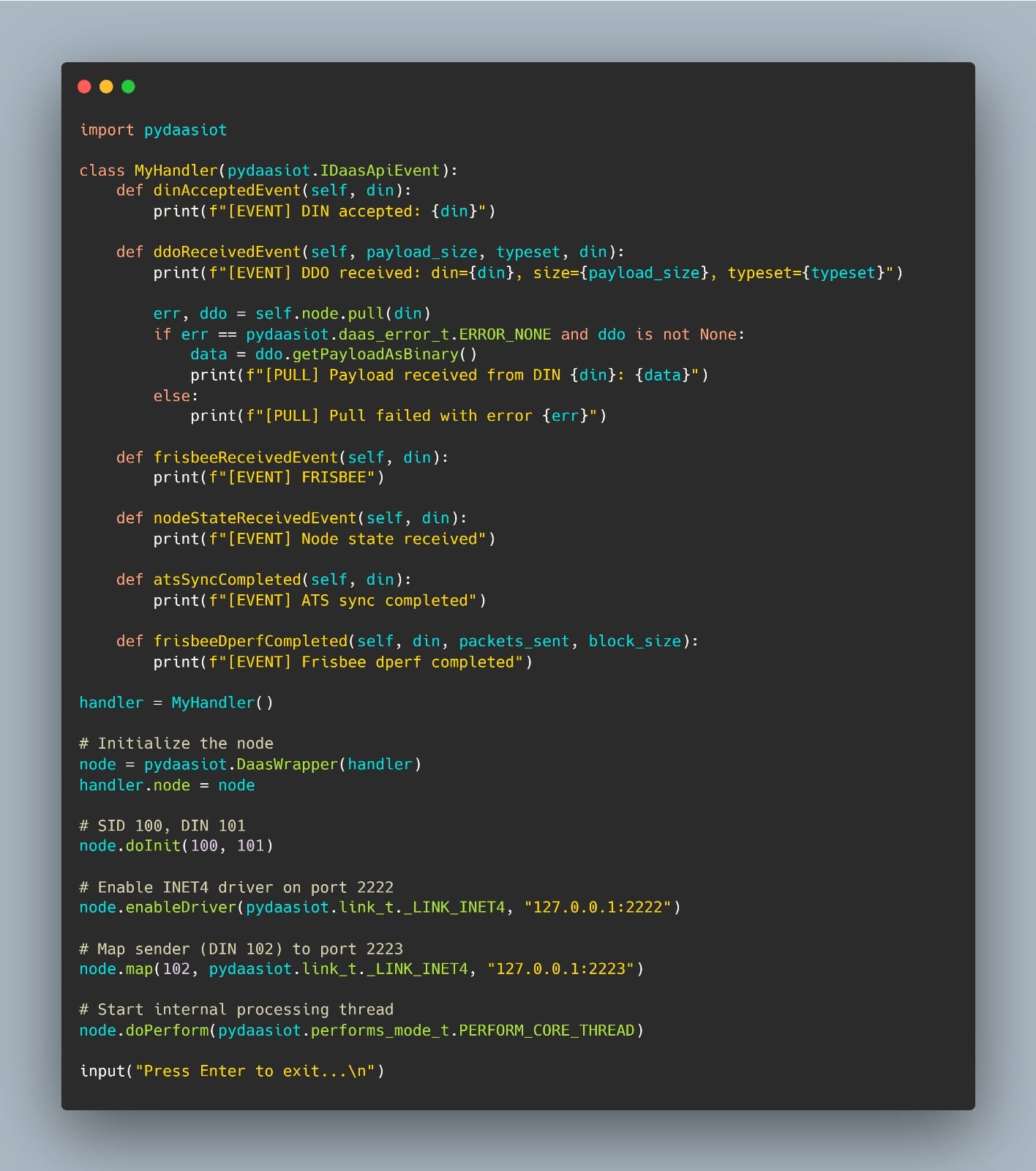
2. A receiver node listen on its own driver port, pulls incoming payloads, and handles them via registered callbacks.
Receiver Node (DIN 101)
Sender Node (DIN 102)
Behind the Scenes
This sender/receiver setup illustrates a few key concepts in action:
- DDO: The core unit of communication. Payloads are encapsulated and routed via node DIN
- DIN/SID: Identifier to uniquely identify nodes and network
- Driver abstraction: Here we use the INET4 over loopback, but Bluetooth and other links are also supported.
- Event-driven architecture: Handlers allow your application to react to incoming data, time sync events, and node state changes.
All of this happens over an overlay network managed by the DaaS-IoT layer – you don’t need to deal with sockets, protocols, or serialization.
Understanding the DIN and SID
In the DaaS-IoT ecosystem, DIN and SID are the two core identifiers that define how nodes are addressed and how communication flows within the overlay network.
DIN (Device Identification Number)
DIN is a unique 32-bit identifier assigned to each node participating in the DaaS-IoT network. It plays a role similar to an address – each packet or DDO is sent from one DIN to another.
DINs are essential for:
- Routing and addressing: every DDO carries both a source and destination DIN
- Session tracking: the runtime uses DINs to maintain active link states and delivery reliability
- Synchronization and discovery: system typesets rely on DINs to coordinate time alignment and topology information
SID (Session Identifier)
SID represents the network domain in which one or more nodes – each identified by a unique DIN are active and can communicate. While the DIN uniquely identifies a single NODE, the SID groups multiple DINs under the same logical network or communication context.
In other words:
- The SID defines the scope of visibility – only nodes within the same SID can discover, synchronize, and exchange DDOs with each other.
- It acts as a namespace or cluster ID, ensuring that different DaaS-IoT networks running in parallel remain isolated
- The DaaS-IoT runtime uses the SID for overlay initialization, time synchronization domains, and state exchange boundaries between DINs
Understanding the Typeset: What It is and How to Use it
A typeset is a 16-bit identifier that labels the type of DDO (Data Delivery Object) being transmitted or received across the DaaS-IoT network. In practice, it tells both the sender and receiver what kind of payload is contained in the packet and how it should be interpreted.
It represents a fundamental attribute of every DDO — you set it when creating a DDO and read it when receiving one.
Understanding the Role of Typesets
Every message exchanged across the DaaS-IoT network is identified by its typeset, which acts as a semantic label describing the data’s purpose.
This mechanism allows nodes to communicate different kinds of information — such as telemetry, configuration, or event notifications — without ambiguity.
A well-defined typeset system ensures that each payload can be correctly decoded, routed, and handled by the appropriate logic, regardless of the physical transport layer or driver in use.
How to use Typesets
Developers can define their own typesets to represent specific data structures or application-level messages.
Each typeset essentially corresponds to a message schema — for example, one for configuration updates, one for sensor telemetry, or one for alert messages.
Typical workflow
- Register your user typesets at startup, assigning each a code (16-bit integer), and optionally an expected payload size for basic validation
- When sending, create a DDO, set its typeset, write the payload, and push it to desired DIN
- When receiving, read the typeset of the incoming DDO and dispatch it to the appropriate handler or decoder
Understanding the DDO
A DDO is the fundamental unit of data exchange in the DaaS-IoT network. Every message, event, or synchronization packet exchanged between nodes is encapsulated inside a DDO, which ensures consistency and reliability across heterogeneous communication links.
Structure and Purpose
Each DDO contains both metadata (such as DINS, typeset, timestamps, and size) and payload data.
The metadata defines how the payload should be interpreted and routed, while the payload holds the actual information.
A DDO can be seen as a self-describing container. It abstracts low-level protocol details, providing a clean interface for sending or receiving data over different drivers (eg. INET4, Bluetooth).
With pydaasiot you can interact with DDOs directly – creating them, writing payloads, and accessing metadata fields.
Key Components
- Typeset → Identifies what kind of message the DDO carries (system or user-defined).
- DIN → The Device Identification Number that uniquely identifies each node in the network.
- Timestamp → Provides timing information used for synchronization and latency estimation.
- Payload → The binary content of the message, interpreted according to the typeset.
- Size → Total length of the payload in bytes.
Lifecycle of a DDO
- Creation – The sender node constructs a DDO object, sets its typeset, attaches a payload, and prepares it for transmission.
- Transmission – The DDO is serialized and sent through the driver layer to a destination DIN
- Reception – The receiver node reconstructs the DDO, reads its metadata, and triggers an event callback
- Handling – Based on the typeset, the DDO is dispatched to the correct decoder or handler logic in the user application.
This lifecycle allows DaaS-IoT to function as a unified overlay protocol, decoupling user logic from physical transport and providing deterministic behavior across different link types.
Understanding the Frisbees
Frisbees are lightweight system messages periodically exchanged between nodes. Its role is similar to a ping – it verifies connectivity, monitors link quality, and helps maintain synchronization between DINs within the same SID.
Frisbees serve as heartbeat and synchronization signals. When a node sends a Frisbee, it expects a response from an other active node in the same SID.
This simple mechanism provides several key functions:
Connectivity Check
Verifies that nodes are reachable and responsive within the network.
Latency Estimation
Measures round-trip time between nodes for performance monitoring.
Clock Synchronization
Helps maintain time alignment across distributed nodes.
Network Awareness
Provides topology information and node availability status.
Ready to Try It?
You can get started today:
For updates and support, visit the PyPI page.

Leave a Reply